Hyper-Threading & Physical Threads
1. CPU structure#
Single core CPU:
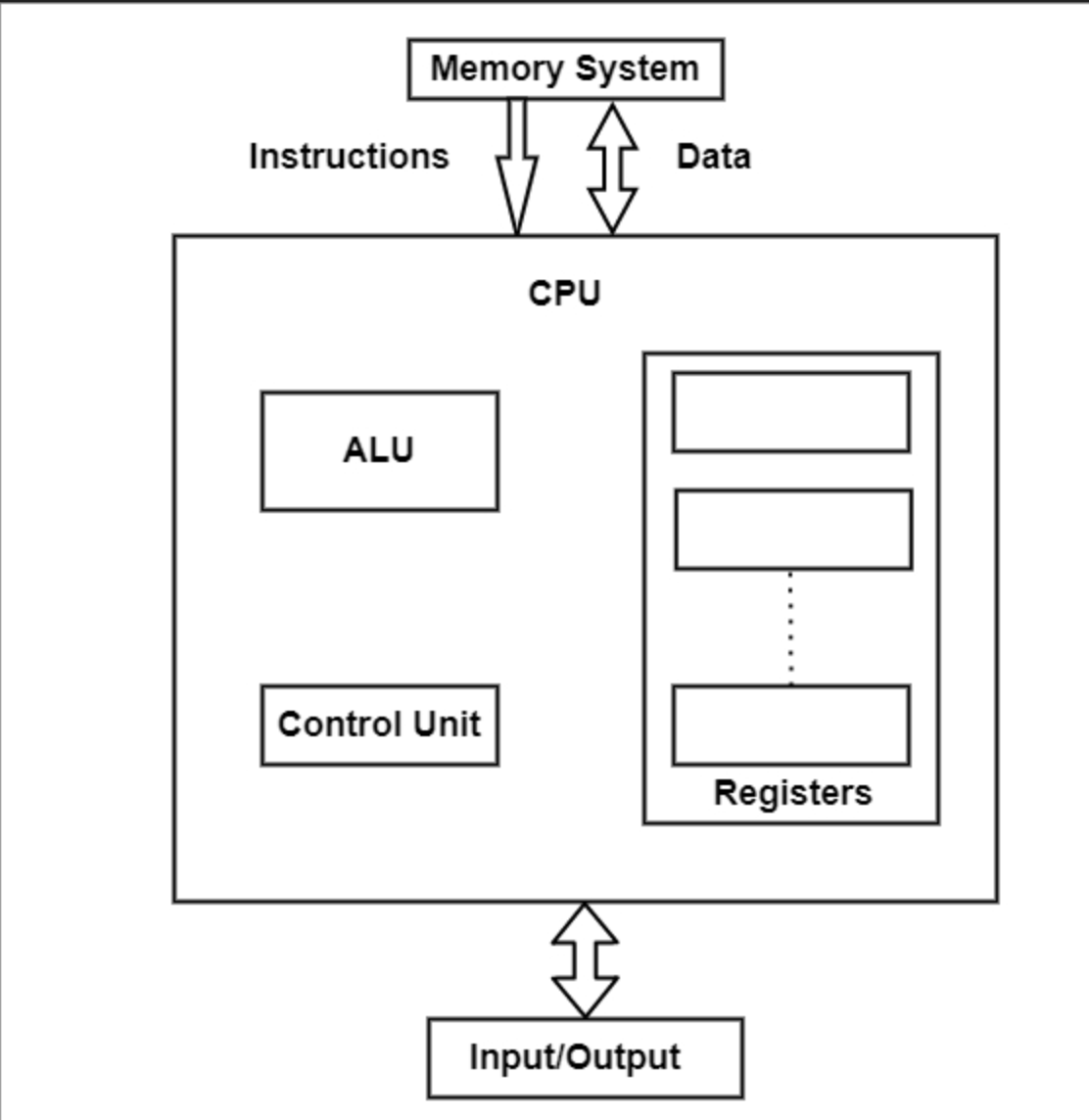
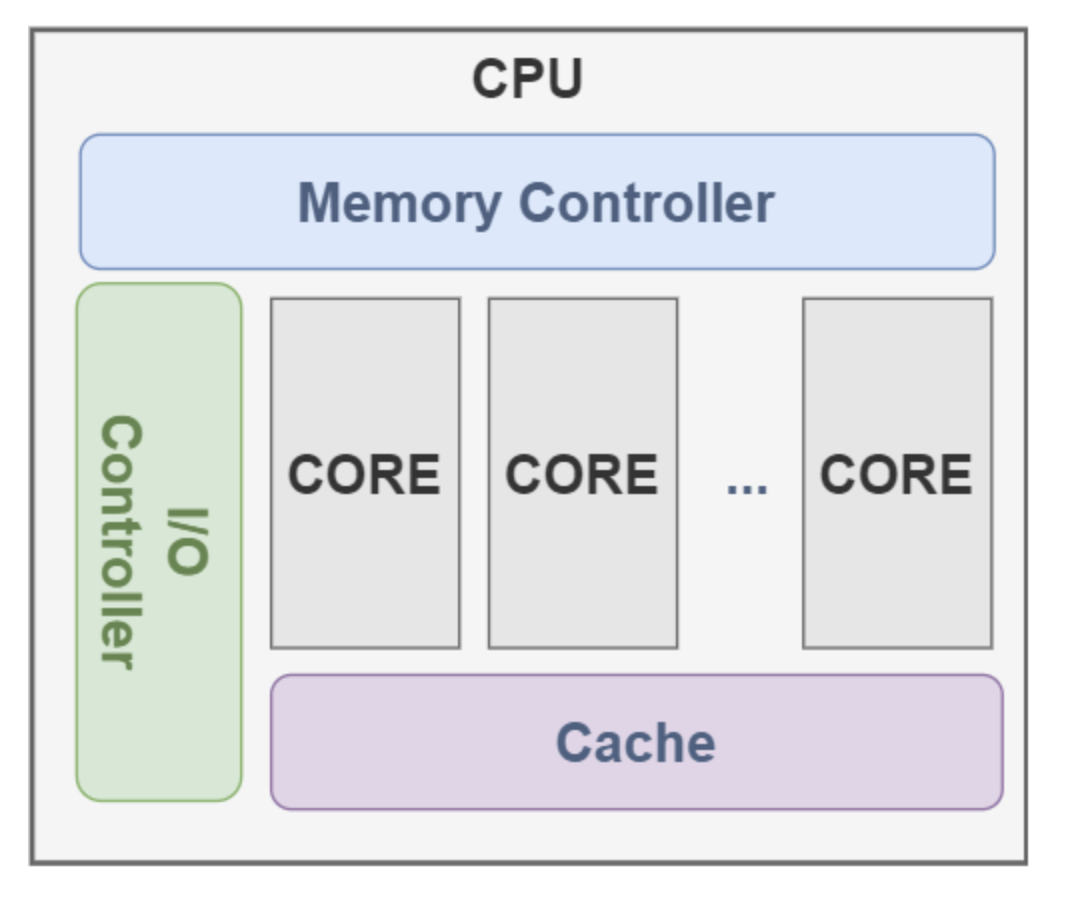
The CPU core consists of three parts: ALU, CU and Memory (Register + Cache), The multiple cores CPU has more than one core (ALU, CU, Memory (Register + Cache)) to execute instructions:
2. Hyper-threading#
A single physical core with hyper-threading or simultaneous multithreading technology appears as two logical cores to an operating system. The CPU is still a single CPU, so it’s a little bit of a cheat. This can speed things up somewhat — if one virtual CPU is stalled and waiting, the other virtual CPU can borrow its execution resources.
Most processors can use a process called simultaneous multithreading or, if it’s an Intel processor, Hyper-threading (the two terms mean the same thing) to split a core into virtual cores, which are called threads. For example, AMD CPUs with four cores use simultaneous multithreading to provide eight threads, and most Intel CPUs with two cores use Hyper-threading to provide four threads.
Some apps take better advantage of multiple threads than others. Lightly-threaded apps, like games, don’t benefit from a lot of cores, while most video editing and animation programs can run much faster with extra threads.
Note: Strictly speaking, only Intel processors have hyper-threading, however, the term is sometimes used colloquially to refer to any kind of simultaneous multithreading.
The Windows Task Manager shows this fairly well. Here, for example, you can see that this system has one actual CPU (socket) and 8 cores. Simultaneous multithreading makes each core look like two CPUs to the operating system, so it shows 16 logical processors.

Logical core vs OS thread#
-
OS Thread(操作系统线程):
- 线程由操作系统内核管理,它可以调度线程在不同的 CPU 核心或逻辑处理器上运行。
- 线程的调度和管理涉及 context switching, priority scheduling
-
Hyper-threading(超线程):
- Hyper-threading 是 Intel 提供的一种硬件级别的技术,它允许单个物理 CPU 核心模拟出两个逻辑处理器。
- 当启用 Hyper-threading 时,操作系统会看到比实际物理核心数更多的处理器。例如,一个拥有 4 个物理核心的 CPU 可能会显示为 8 个逻辑处理器。
在操作系统管理线程的过程中,它会将多个 OS thread 分配给可用的 CPU 核心,包括通过 Hyper-threading 技术创建的逻辑处理器。这个分配过程考虑了多个因素,包括线程的优先级、CPU 亲和性(affinity)、以及核心的当前负载情况。因此,操作系统线程与 Hyper-threading 是协同工作的两个不同层面的概念:一个属于软件层面(操作系统管理),另一个属于硬件层面(CPU 架构)。
参考: