SwiftUI Modifiers
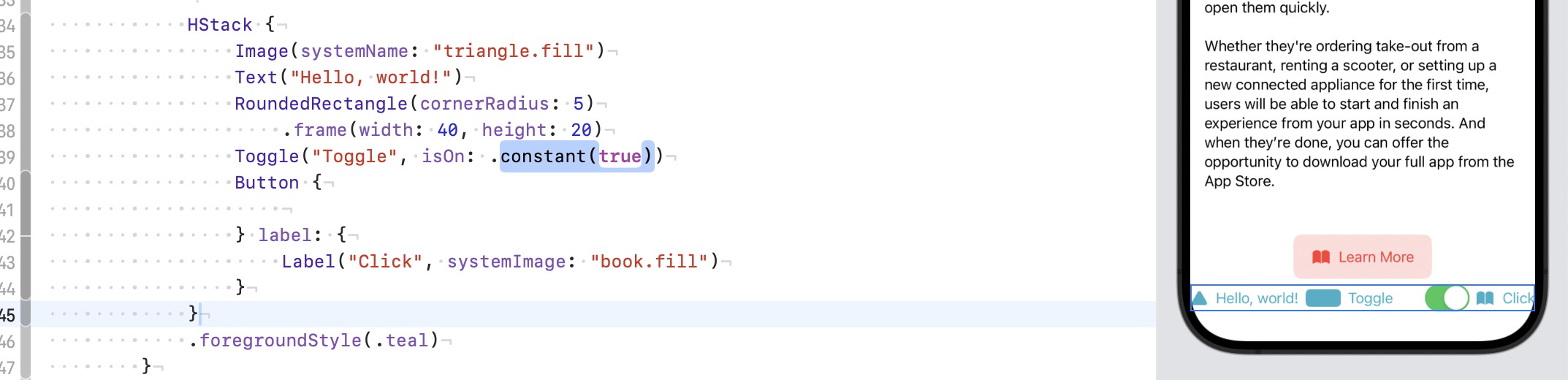
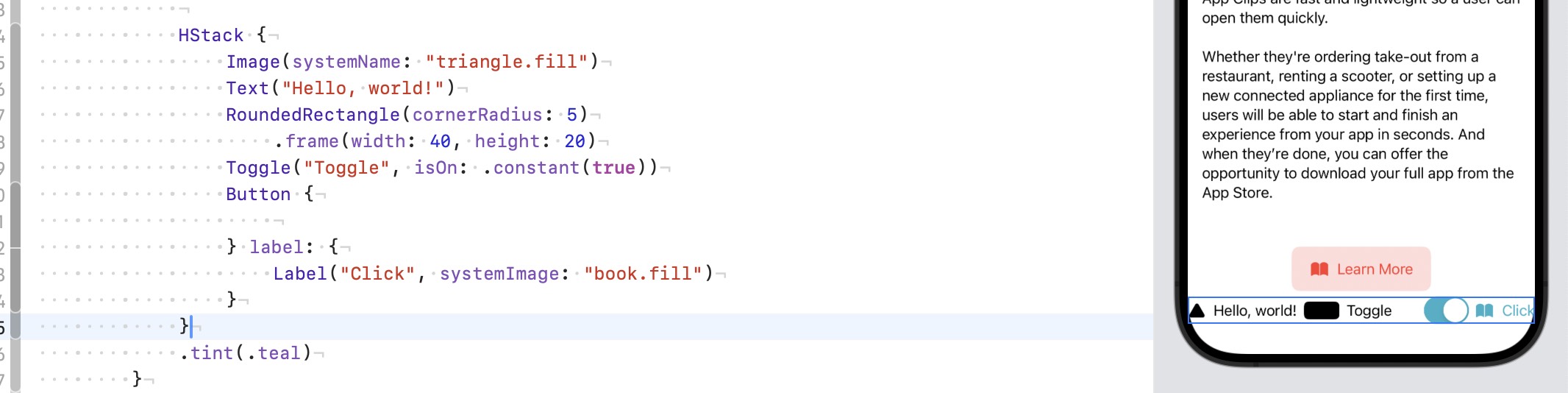
1. .foregroundStyle() and .tint()#
.tint- Targets: Works mainly on interactive controls like
Button,Toggle,Picker, etc. - Effect: Changes the color of text and icons within these controls, but usually doesn’t affect plain
Textviews or other non-interactive elements.
- Targets: Works mainly on interactive controls like
.foregroundStyle()- More versatile, it changes the style (not just the color) of all foreground elements within a view hierarchy, including text, icons, shapes, etc.
2. Other Common Used Modifiers#
2.1. Text Modifiers#
.font():.largeTitle,.title,.title2,.headline,.subheadline,.body,.footnote,.font(.system(...))
2.2. Image Modifiers#
.resizable(), .scaledToFit(), .scaledToFill(), aspectRatio(contentMode: .fill), imageScale()
Note
.frame()must be used after.resizable(), because image is not resizable by default.
.scaledToFit()and.scaledToFill()should be used before.frame(), if used after.frame(), it will not work.
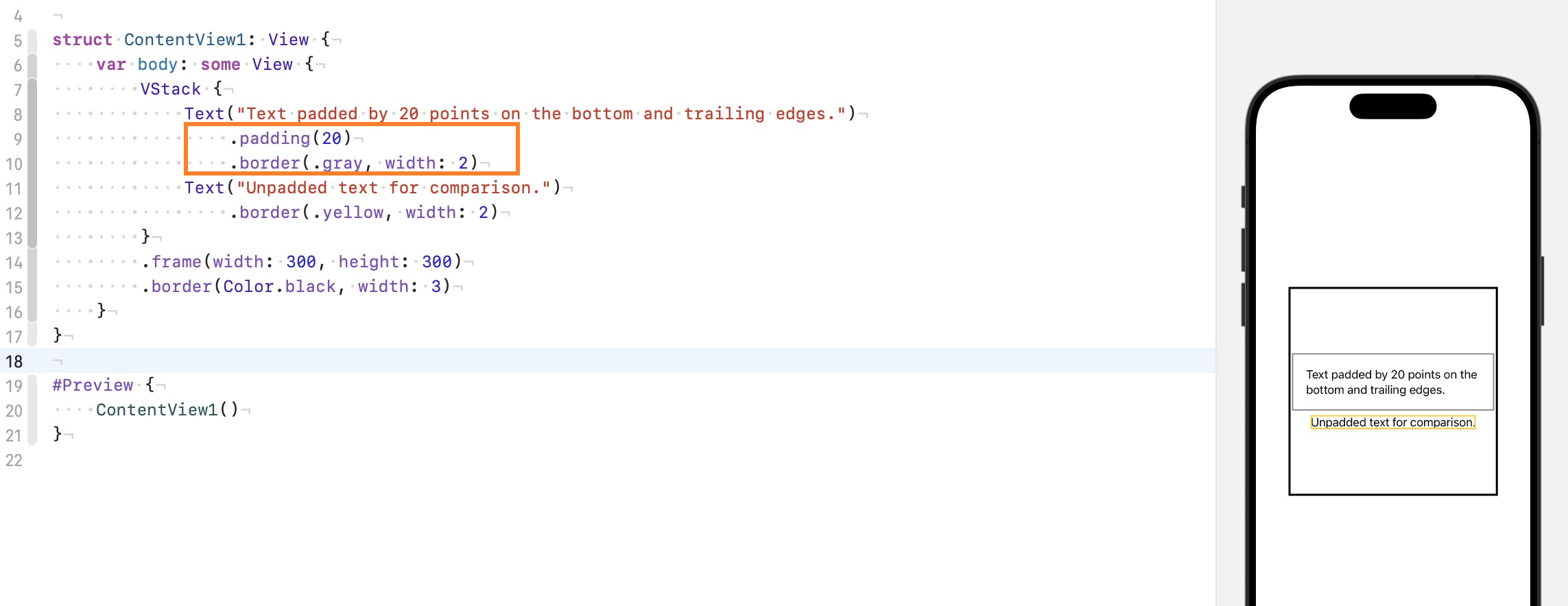
3. padding()#
Adds an equal padding amount to specific edges of this view.
padding 不要理解成 css 中的 padding 内边距, 在 swiftui 中它更像是一个外边距, 应用哪个 view 上面, 就会为其产生外边距, 而不是内侧. 我们看一下 padding 的词典解释: soft material such as foam or cloth used to pad or stuff something. 填充的东西, 比如在亚马逊买的杯子, 快递盒子里面有个泡沫, 泡沫里面才是 杯子, 而这个泡沫就是被子的 padding. 所以应用 padding modifier 的顺序也是至关重要.
原理: The padding modifier adds padding to a view. It does so by taking the proposed size and subtracting the padding.
解释:
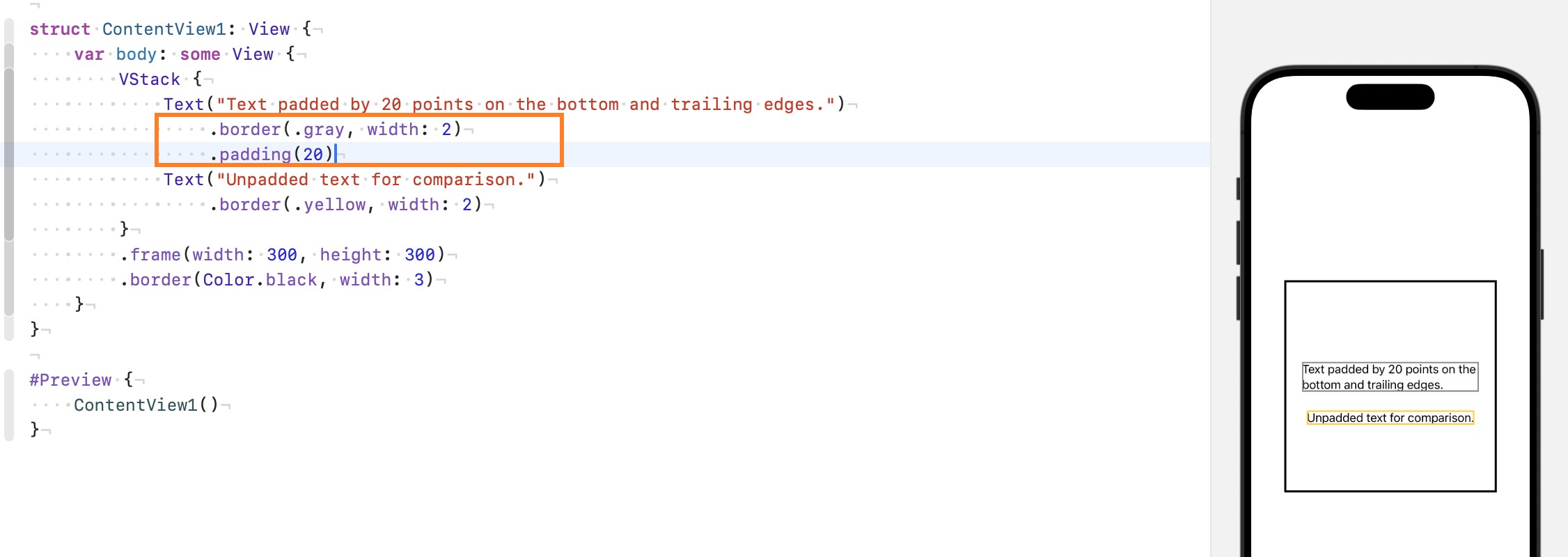
- SwiftUI布局是一个自上而下的过程, 父视图向 padding 提议一个可用的尺寸(proposed size)如 30
padding收到 proposed size: 30, 会减去 16(默认) = 14, 将 proposed size = 14 传给子视图- 原始视图基于这个较小的建议尺寸来决定自己的大小 (可以遵从或者不遵从, 取决与 view 的类型和应用的 modifier, 如
.fixedSize()就会让 view 一直 report 理想的尺寸, 而不是父视图 propose 的尺寸)
4. .aspectRatio(1, contentMode: .fit) 和 .resizable()#
.aspectRatio() 最常见的就是和 .resizable() 一起使用.
4.1. .resizable()#
func resizable(
capInsets: EdgeInsets = EdgeInsets(),
resizingMode: Image.ResizingMode = .stretch
) -> Image
// stretch: A mode to enlarge or reduce the size of an image so that it fills the available space.
所以应用了 resizable 的图片, 大小是根据可以用空间改变的, 这里的可用空间也可以理解为父视图为其 propose 的尺寸.
如下, 图片默认, 是不接受父视图的 propose size, 只会 report 自己的 size.
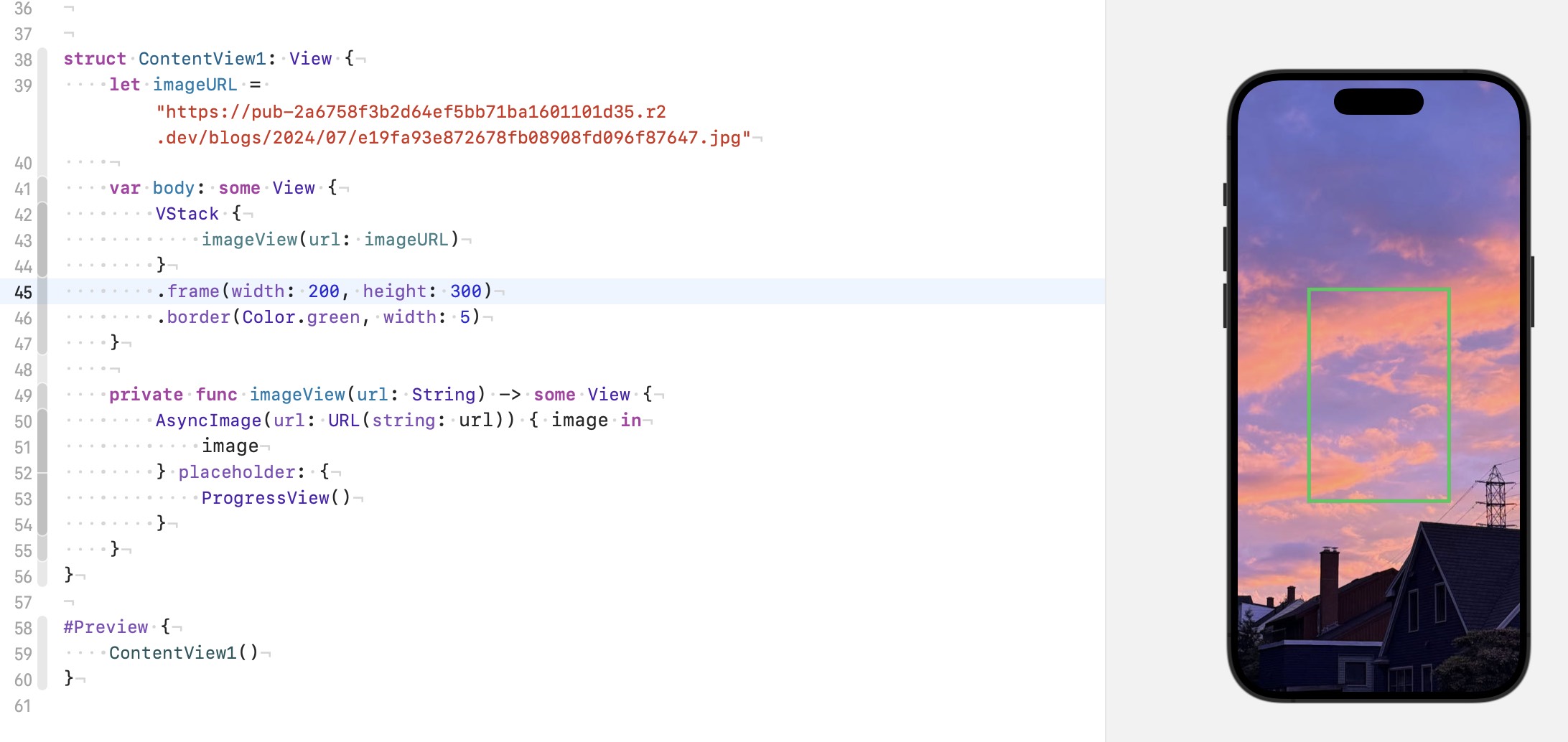
加上 resizable, 图片便会接受 proposed size, 而 aspectRatio(...) 刚好就是修改 proposed size 的 (根据指定比例), 它俩天生一对.
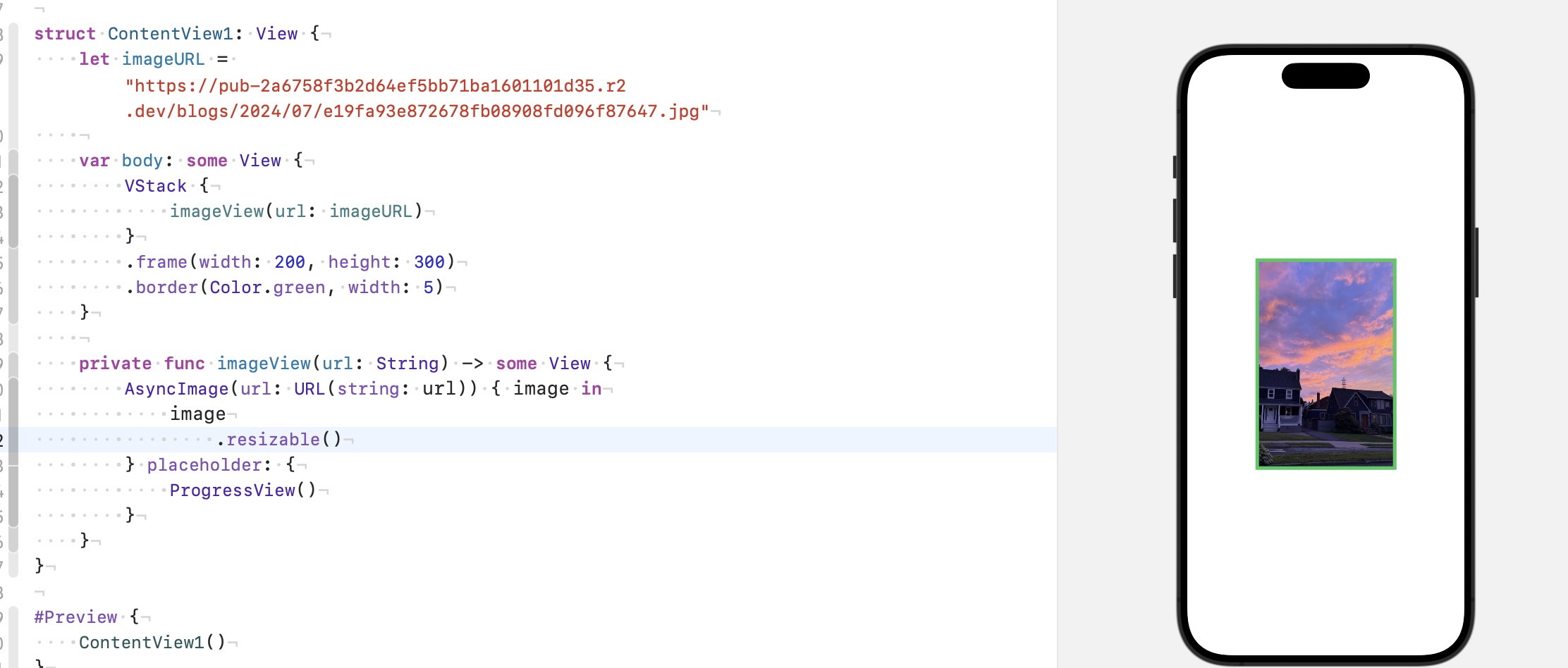
比如我让图片的比例显示为正方形:
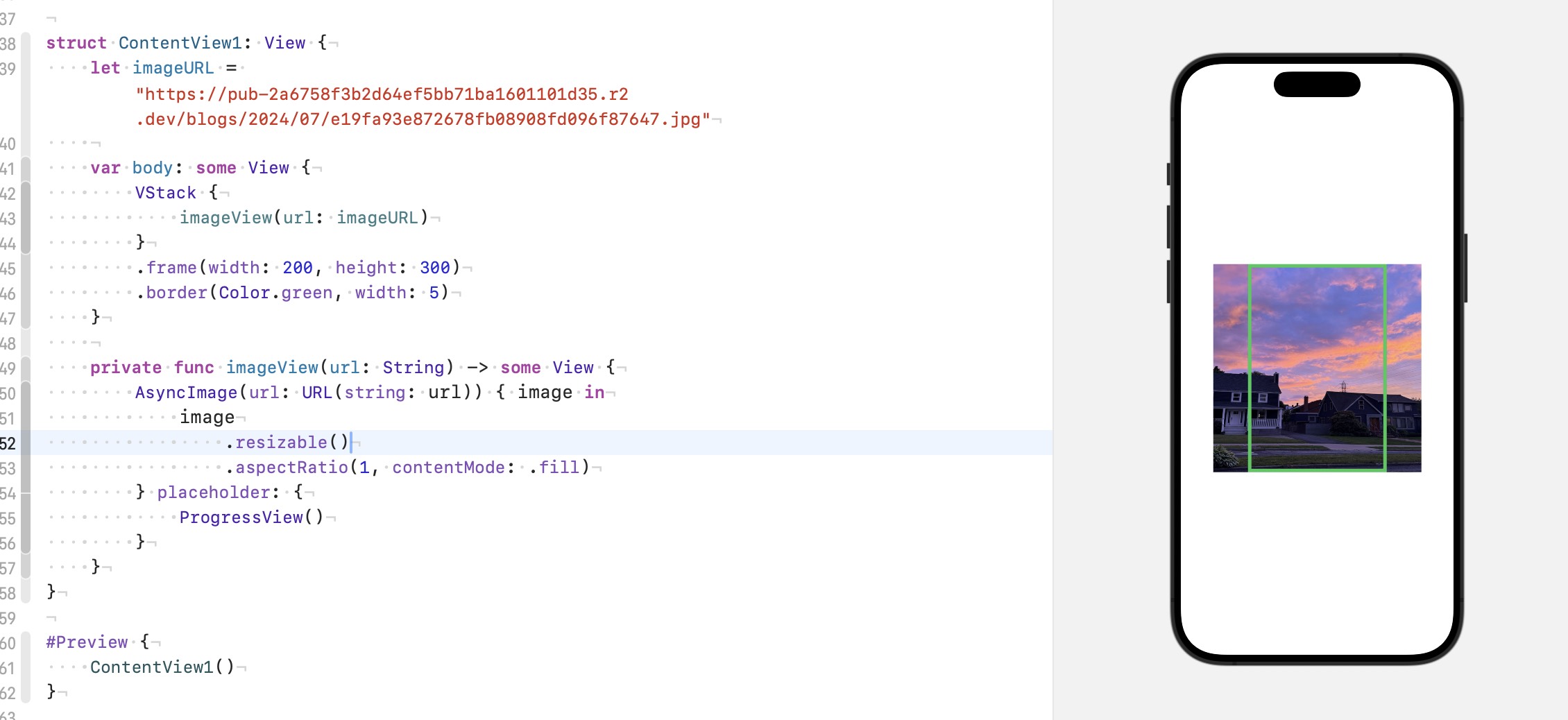
虽然是正方形了, 宽高比为 1:1, 可能会问, 不是说 resizable() 让图片接受 propose size 吗, 为什么还是超出了 frame, 你仔细看清楚, 图片的直接上级是 aspectRatio(...) 而不是 VStack 的 frame, frame 给 vstack 一个 propose size, 然后 vstack 再把这个 size 传递给 aspectRatio(...), 即 width: 200, height: 300, 然后我们给 aspectRatio(...) 的参数是 .fill, 宽高比为 1, 所以 aspectRatio(...) 修改 propose size 为 300 * 300 给 image, 因此呈现了现在的结果, 此时可以配合 .clipShape() 剪切掉图片多余的部分.
4.2. aspectRatio(...)#
-
第一个参数是宽高比(可选), 若不提供, 则向上级 report 子视图理想的宽高比.
-
第二个参数
contentMode: A flag indicating whether this view should fit or fill the parent context.
看个例子就明白了:


Note: In the initial image example, we didn’t specify a fixed aspect ratio. By leaving the parameter off, the underlying view’s ideal size is used to compute the aspect ratio. To compute the ideal size, the aspect ratio first proposes a
nil×nilsize to its child. The child’s ideal size is used as the aspect ratio, and the aspect ratio then either fits or fills a rectangle with the computed ratio within its proposal. swiftuifieldguide.com
.fill 常与.clipShape()搭配使用. 当你想确保 frame 被完全填满, 不留空白时使用
fit 适应 frame, 当打算显示整个图像, 不丢失任何部分时使用
4.3. Gotchas #
Perhaps surprisingly, the aspect ratio modifier only changes the proposal. For example, in the view below, it’ll propose a square size to the text. However, as we can see from the border, the aspect ratio directly reports its child’s size, and it doesn’t report a square size.
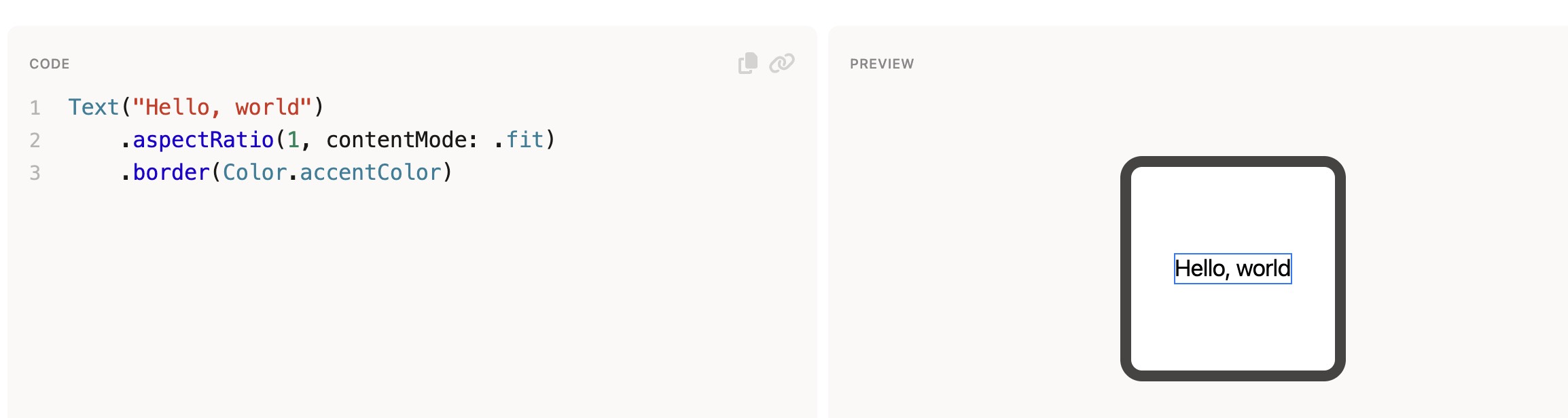
上面这句话中的 proposal 和 report 是什么?
The essence of SwiftUI’s layout system is very simple: a parent proposes a size to its child, and the child reports a size.
发现一个动画很清楚的解释了这一过程, 可以去查看, 如果不是很理解可以看这个视频: How layout works in SwiftUI
All SwiftUI layout happens in three simple steps, and understanding these steps is the key to getting great layouts every time. The steps are:
- A parent view proposes a size for its child.
- Based on that information, the child then chooses its own size and the parent must respect that choice.
- The parent then positions the child in its coordinate space.
再看最上面那句话: the aspect ratio modifier only changes the proposal, 显然这是在说 aspect ratio modifier 只会偷偷修改建议尺寸的大小(比例), 但是孩子上报的尺寸 他会如实上报, 即我把我的建议尺寸给你, 接不接受就看你自己了. 且 swiftui 的逻辑是, 上级视图必须无条件接受(上报)下级尺寸的报告.
了解更多: Aspect Ratio - SwiftUI Field Guide
References:
Aspect Ratio - SwiftUI Field Guide
Introduction - SwiftUI Field Guide
5. Flexible Frames#
A flexible frame allows us to specify a minimum, ideal, and maximum value for each dimension. We can think of a frame as a “wrapper” view around its child that can both change the proposal to its child and change the reported size. One the most common usages is using maxWidth: .infinity to fill up the available width.
One the most common usages is using
maxWidth: .infinityto fill up the available width. 注意, 是 maxWidth 不是 width.
frame 的默认宽度是其子视图的 report width, 若指定 maxWidth: .infinity , 则 frame 会填满父视图, 若父视图宽度小于子视图的 report width, frame 的宽度将保持在 子视图的 report width, 类似 [child’s report width, .infinity)
可以使用 minWidth: 0, 无条件接受父视图的宽度,
If we want to unconditionally accept the proposed width (regardless of the content’s width), we can specify a minimum width of
0and a maximum width of.infinity.
References: Flexible Frames - SwiftUI Field Guide
5. 实例分析#
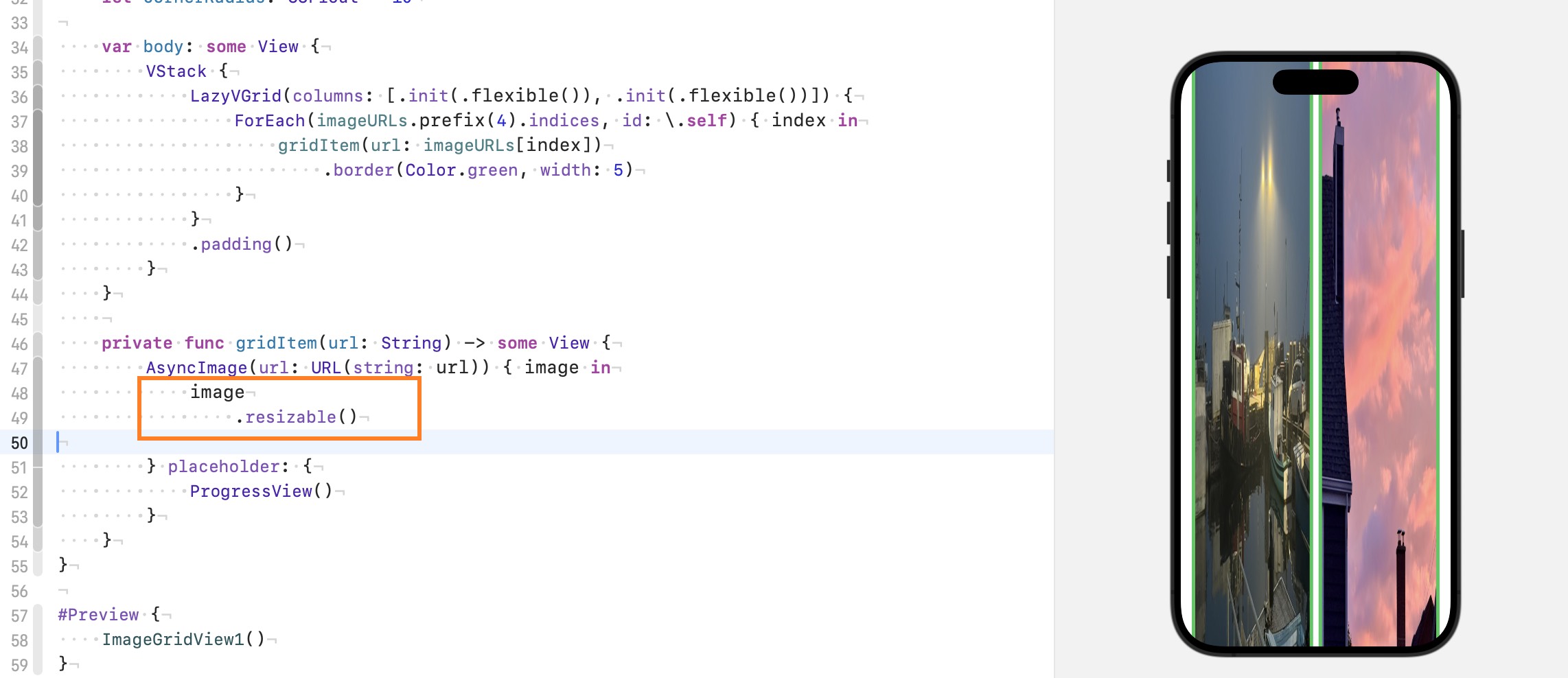
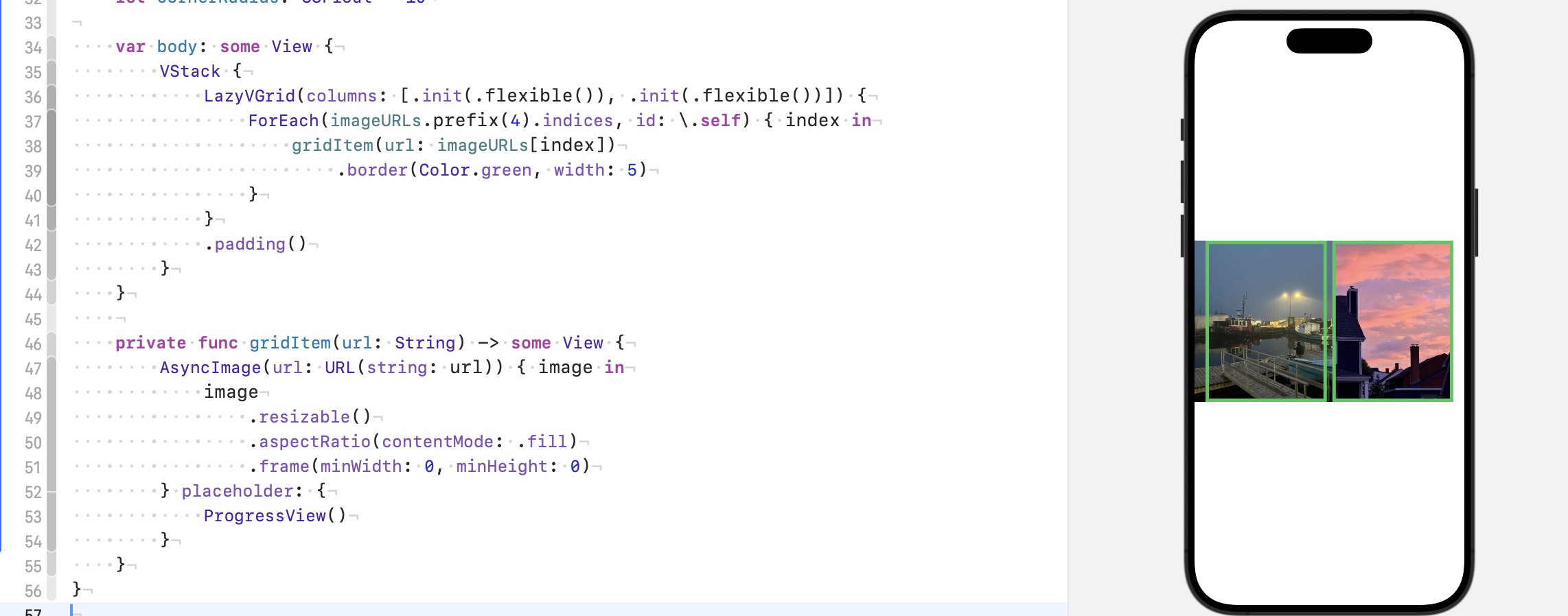
前面了提到了 .resizable() 的默认行为: A mode to enlarge or reduce the size of an image so that it fills the available space. 宽度被 LazyVGrid 平均分配好了(两列), 图片想要填满屏幕, 就被纵向拉伸, 变成上图的样子.
加下来我们使用 .aspectRatio(contentMode: .fill), 前面也提到了 .aspectRatio() 会根据比例修改 propose size, 我们没有指定比例, 所以比例就是原图的比例, 因为宽度确定了, 所以为了保持原图的比例, 图片自然就变得没那么长了. 如下图:

可是为啥宽度不一样呢? 很简单, 左边的图比较宽, LazyVGrid 会给每行分配相同的高度, 也就是两张图的 .aspectRatio() 接受到的高度是相同的, 但是比例不同(各自图片的比例), .aspectRatio() 会根据现在的宽度高度和比例来修改修改后的 propose size (如192*158) 肯定也不同, .resizable() 会完全接受 propose size, 所以两张图的宽度不同,
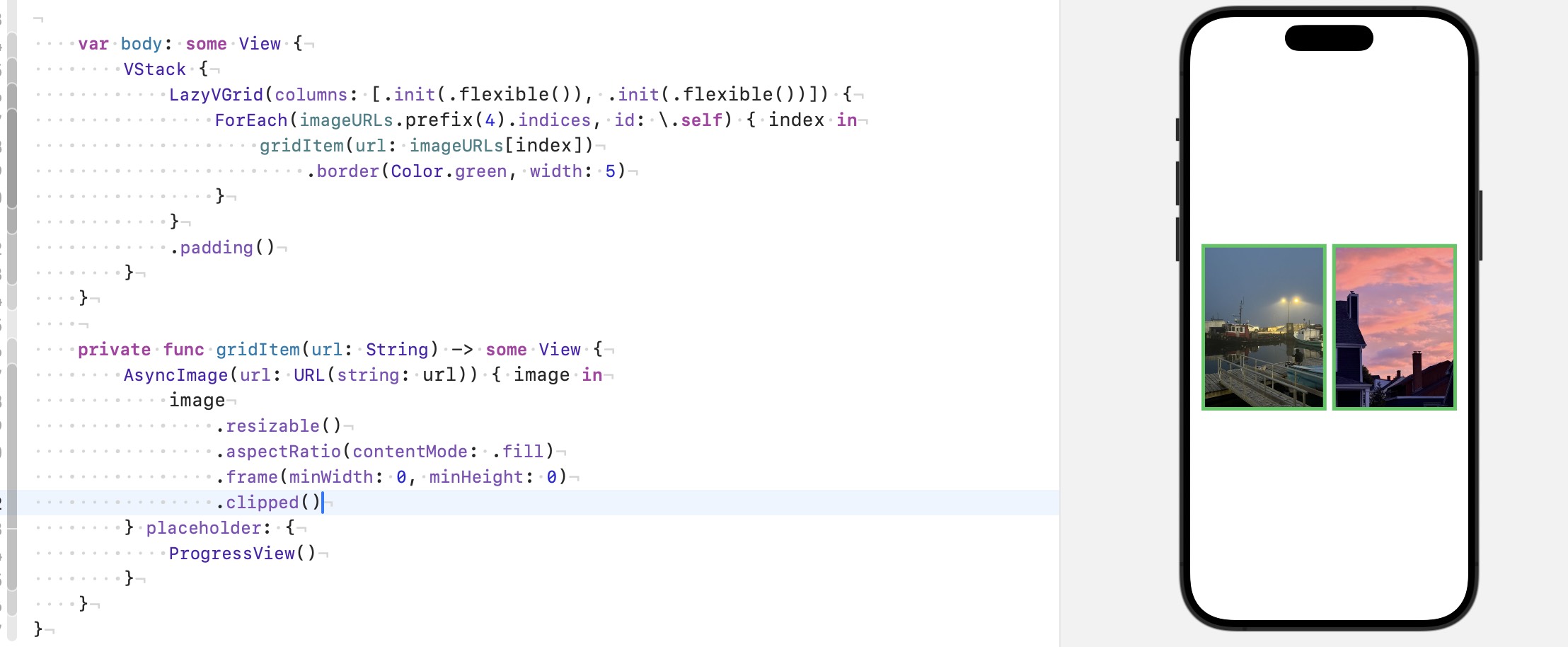
想让宽度相同, 可以给相同的比例:
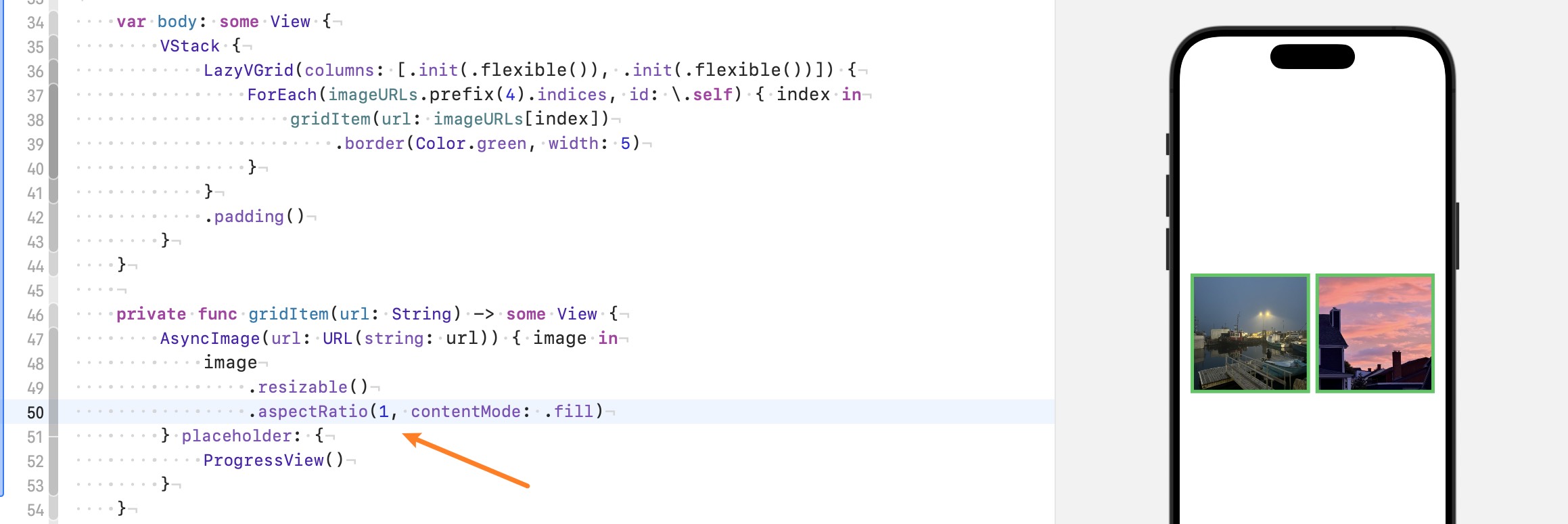
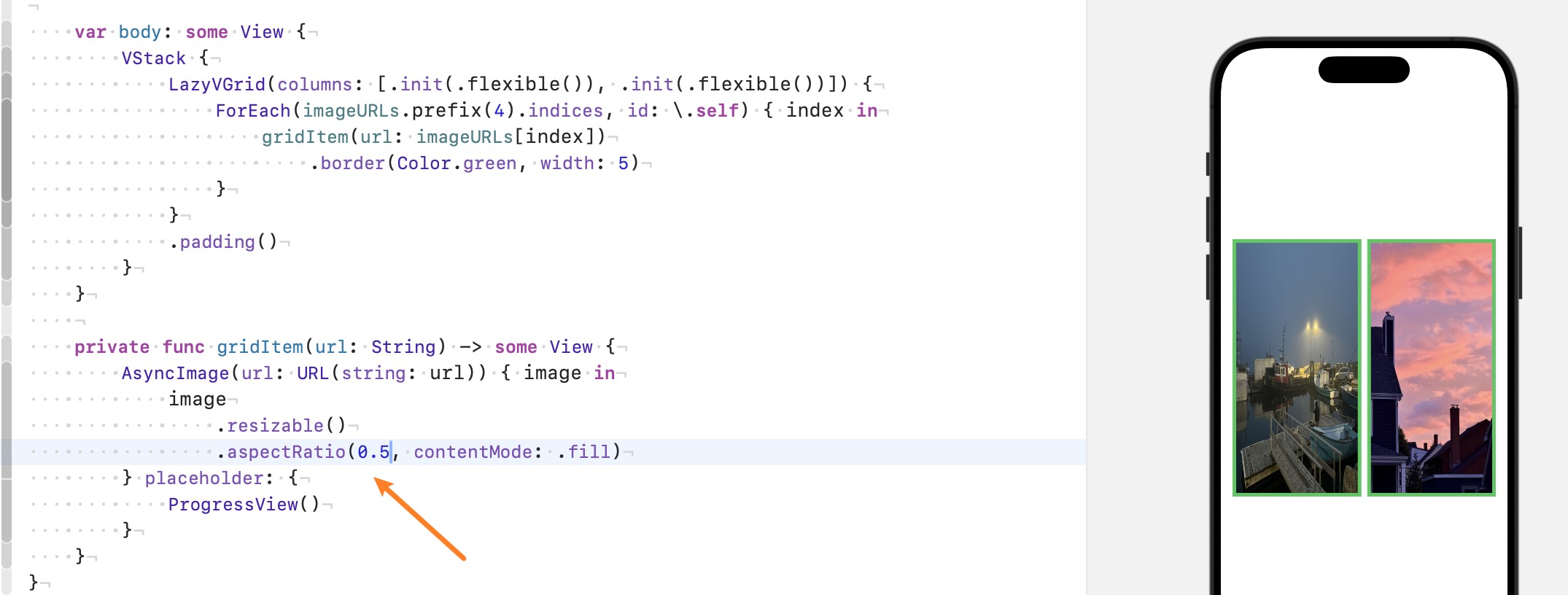
但如果我们不想让图片被拉伸, 想保持原图的比例呢, 那就使用 Flexible Frame, 提供 minWidth: 0, 意思是无条件接受上级propose width, 因为我们两列都是 flexible: [.init(.flexible()), .init(.flexible())], LazyVGrid 分配的宽度自然也相同, frame 就得到了相同的宽度, 前面提到了 frame 会修改 report size from child, 也就是说无论 child 的尺寸是多少, frame 都会向上级报告自己的尺寸,
当然 .aspectRatio() 会修改 frame 传递的尺寸, 因为有比例存在, 这没关系, 我们最后在 frame 上使用 clip 就好了.